Newsletter
What’s in a number when it comes to GHG Emissions?

In the case of Summerside, the number is 2.7, and that’s impressive! Let us tell you how we’re getting there.
The City of Summerside is committed to pioneering sustainable solutions for mitigating climate change and enhancing community resilience. In the 2021 Census of Population conducted by Statistics Canada, Summerside had a population of 16,001 living in 7,097 of its 7,393 total private dwellings, an increase of 7.8% from its 2016 population of 14,839. With a land area of 28.21 km2 (10.89 sq mi), it had a population density of 567.2/km2 (1,469.1/sq mi) in 2021.
Summerside is widely recognized as a leader and early adopter of green technologies. Their unique municipally-owned infrastructure, combined with a business environment that encourages innovation, sets them apart from many other communities in Atlantic Canada. Summerside energy production is projected to be primarily renewable by 2024, much of which is being produced within the city's boundaries. The city's ambitious goals align with Prince Edward Island’s (“PEI”) commitment to the Net-Zero Carbon Act and the Nationally Determined Contributions of Canada in the Paris Agreement
As part of that commitment, Summerside recently commissioned a Greenhouse Gas Emission Inventory Report. This study aims to comprehensively identify and model greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions across the city. By doing so, it lays the groundwork for a nuanced understanding of the sources and patterns of emissions, providing a foundation for informed decision-making. The study goes beyond mere analysis; it actively seeks out opportunities for GHG reduction throughout the region. By exploring and developing strategies to curtail emissions, the city is not only adapting to the challenges posed by climate change but also positioning itself as a leader in sustainable development.
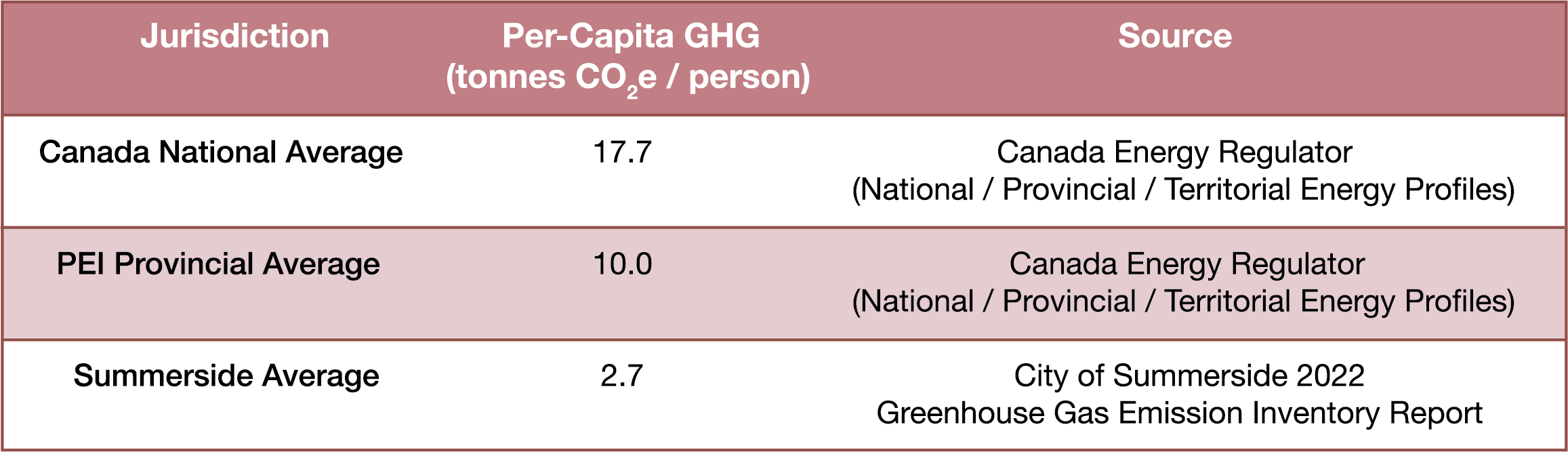
The GHG emissions, as measured and reported through the GHG GPC (Greenhouse Gas Protocol) Standard, underscored the commitment to transparent and standardized methodologies in assessing environmental impacts across diverse sectors. Emissions are disaggregated by sectors, including energy, transportation, industrial processes, waste, and land use. This analysis pinpoints major emission sources within each sector, aiding in prioritizing mitigation efforts. The following table summarizes the emission per capita in Summerside as compared to Canada and Prince Edward Island.
Summerside is widely recognized as a leader and early adopter of green technologies. Their unique municipally-owned infrastructure, combined with a business environment that encourages innovation, sets them apart from many other communities in Atlantic Canada. Summerside energy production is projected to be primarily renewable by 2024, much of which is being produced within the city's boundaries. The city's ambitious goals align with Prince Edward Island’s (“PEI”) commitment to the Net-Zero Carbon Act and the Nationally Determined Contributions of Canada in the Paris Agreement
As part of that commitment, Summerside recently commissioned a Greenhouse Gas Emission Inventory Report. This study aims to comprehensively identify and model greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions across the city. By doing so, it lays the groundwork for a nuanced understanding of the sources and patterns of emissions, providing a foundation for informed decision-making. The study goes beyond mere analysis; it actively seeks out opportunities for GHG reduction throughout the region. By exploring and developing strategies to curtail emissions, the city is not only adapting to the challenges posed by climate change but also positioning itself as a leader in sustainable development.
The GHG emissions, as measured and reported through the GHG GPC (Greenhouse Gas Protocol) Standard, underscored the commitment to transparent and standardized methodologies in assessing environmental impacts across diverse sectors. Emissions are disaggregated by sectors, including energy, transportation, industrial processes, waste, and land use. This analysis pinpoints major emission sources within each sector, aiding in prioritizing mitigation efforts. The following table summarizes the emission per capita in Summerside as compared to Canada and Prince Edward Island.

2022 was a turning point
in Summerside’s Journey
2022 was a turning point in the community’s emission reduction achievements. Summerside's GHG emissions were significantly reduced compared to previous years due to the integration of renewable energy sources. The city has assembled partners with a shared vision, all of whom are dedicated to creating an infrastructure that is ideal for real-world testing and economic verification of innovative green technologies. This initiative is part of Summerside's broader Open Innovation Ecosystem, positioning the city as a leader and one of the early adopters of green technologies in the province.
The city’s top three sources of community GHG emissions are 1) electricity usage in institutional / commercial / industrial buildings; 2) industrial processes and product use (refrigerant release); and 3) waste generated by the City.
Despite its many strengths, Summerside faces its own set of challenges. Like many coastal communities, the city is not immune to the impacts of climate change. Rising sea levels and extreme weather events pose a potential threat to its coastal areas, requiring strategic planning and sustainable development practices to mitigate risks and build resilience.
The city is beginning to address these challenges by implementing renewable energy and greener technologies, encouraging sustainable development, and quantifying its carbon footprint.
Opportunity Areas
The city’s top three sources of community GHG emissions are 1) electricity usage in institutional / commercial / industrial buildings; 2) industrial processes and product use (refrigerant release); and 3) waste generated by the City.
Despite its many strengths, Summerside faces its own set of challenges. Like many coastal communities, the city is not immune to the impacts of climate change. Rising sea levels and extreme weather events pose a potential threat to its coastal areas, requiring strategic planning and sustainable development practices to mitigate risks and build resilience.
The city is beginning to address these challenges by implementing renewable energy and greener technologies, encouraging sustainable development, and quantifying its carbon footprint.
Opportunity Areas
- Carbon Offsets
- Electrification of Heating Systems
- Local Agriculture
- Electrifying Municipal Fleet and Investing in Electric Vehicle Infrastructures
- Waste Diversion
- Residential energy reduction projects
At 2.7 tonnes, Summerside is leading the way on GHG emissions on a per capita basis in PEI and looks to further implement innovation and adaptation to drive that number lower. Given the opportunities and direct link to economic development, growth, and sustainability, Summerside is poised to further collaborate with industry to help the community reach new heights in the fight against emissions.

Clean Tech Roadmap
Summerside eagerly pursues clean development projects with determination and enthusiasm. Its municipally-owned utility, Summerside Electric, uniquely positions the city to advance clean energy, energy storage, and electrification opportunities. The city has a proven track record of collaborating effectively with industry and a strong knack for innovative approaches to problem-solving, causing Summerside to emerge as a cleantech leader. Beyond its tremendous commercial advantages, Summerside is also a great place to live and work. Housing and real estate costs in PEI are among the lowest in the country, and subsequently, it has one of the highest homeownership rates in North America. The quality of life is second to none, with short commute times, access to sandy beaches, incredible food, and a rich cultural heritage.
Summerside possesses considerable strengths and opportunities that lend themselves well to promoting and further developing its cleantech sector. The city holds 13% of PEI’s total jobs and GDP and 11% of the province’s clean jobs and GDP. Summerside has invested significantly in sustainable infrastructure and energy-efficient practices, leveraging funds and support from federal and provincial governments. Notably, it houses Atlantic Canada's first certified passive energy-designed industrial facility. The city also hosts the innovative Summerside Business Commons Eco Park, aiming to foster critical mass, combining the integration of light manufacturing and office space for aspiring cleantech companies. Additionally, the city maintains a strong commitment to renewable energy with projects like Summerside Sunbank, which will raise its total renewable generation capacity to 63% of Summerside’s needs upon completion, which is scheduled for early 2024.
Another advantage is the city’s small size, which enables a level of nimbleness and agility not found in larger municipalities within Canada, where additional bureaucratic processes may bog down projects. This trait allows a project to transition from conception to implementation quickly. Summerside also boasts a strong risk tolerance for trying new things and has created a supportive business and political environment that speaks to the needs of cleantech businesses. The city’s lower-than-national average workplace turnover rate creates a supportive and loyal business environment. Less turnover increases the profitability of companies, which may often struggle with retention issues when setting up operations in a new market.
Furthermore, the ability to leverage city utilities and other municipal infrastructures (e.g., a fibre optic network) through one efficient channel underscores the benefit Summerside offers companies looking for a location to pilot, demonstrate, and develop clean technology.
Summerside possesses considerable strengths and opportunities that lend themselves well to promoting and further developing its cleantech sector. The city holds 13% of PEI’s total jobs and GDP and 11% of the province’s clean jobs and GDP. Summerside has invested significantly in sustainable infrastructure and energy-efficient practices, leveraging funds and support from federal and provincial governments. Notably, it houses Atlantic Canada's first certified passive energy-designed industrial facility. The city also hosts the innovative Summerside Business Commons Eco Park, aiming to foster critical mass, combining the integration of light manufacturing and office space for aspiring cleantech companies. Additionally, the city maintains a strong commitment to renewable energy with projects like Summerside Sunbank, which will raise its total renewable generation capacity to 63% of Summerside’s needs upon completion, which is scheduled for early 2024.
Another advantage is the city’s small size, which enables a level of nimbleness and agility not found in larger municipalities within Canada, where additional bureaucratic processes may bog down projects. This trait allows a project to transition from conception to implementation quickly. Summerside also boasts a strong risk tolerance for trying new things and has created a supportive business and political environment that speaks to the needs of cleantech businesses. The city’s lower-than-national average workplace turnover rate creates a supportive and loyal business environment. Less turnover increases the profitability of companies, which may often struggle with retention issues when setting up operations in a new market.
Furthermore, the ability to leverage city utilities and other municipal infrastructures (e.g., a fibre optic network) through one efficient channel underscores the benefit Summerside offers companies looking for a location to pilot, demonstrate, and develop clean technology.

Summerside’s Cleantech Leadership Areas:
1. Leveraging its Infrastructure to Accelerate Clean Growth — Summerside leverages its municipally-owned infrastructure and has a clear goal for economic growth by expanding its cleantech sector. The municipally-owned fibre optic network serves as a foundation for enabling energy efficiency and renewable initiatives such as the Heat for Less Now Project – using electric thermal systems and smart grid technologies to save energy and money. Xchange, Summerside's accelerator, offers an unparalleled environment for acceleration, product testing, and validation, with a special emphasis on assisting international start-ups in breaking into the North American market. Projects like the first-in-the-world Industrial Scale Solar Energy Storage System and a North American first end-to-end AI Smart Grid pilot set Summerside apart as a city primed for transformative cleantech endeavours.
2. Embracing Innovation and Nurturing Growth – Over recent years, Summerside has cultivated an ecosystem that celebrates entrepreneurial thinking. Fusing the city’s historic charm with a forward-thinking economic development strategy offers a conducive environment for clean businesses to thrive. The Summerside Business Commons is a testament to this commitment, positioning the city as a nexus where creativity meets sustainability. Situated in the heart of Summerside, this 14-acre Eco-Park boasts seven construction-ready lots equipped with essential infrastructures such as shared parking, phase 3 electrical, and green energy supply. It fosters innovation and success in an environment optimized for productivity and resource conservation.
3. A Hub for Diverse Sectors with a Future-forward Vision – Summerside is pushing to be Canada’s first Net Zero City and has taken an all-hands-on-deck approach, with cleantech solutions being core to the city’s economic development strategy. Summerside is on a trajectory of significant growth, with several key clean development projects underway, including satisfying the city’s energy needs with 100% renewable energy and developing the backbone infrastructure for green hydrogen production generation and fuelling stations.
Summerside has strategically decided to use the transition towards a low-carbon economy as an opportunity to develop and invest in its clean technology sector. The city is in alignment with the provincial 2040 Net Zero Framework, which further positions the city as a reliable partner and location for cleantech development and deployment. For international companies aspiring to enter the Canadian or North American market, Summerside can serve as an attractive option, offering a high-quality, supportive ecosystem and a supportive first buyer/customer opportunity. This can facilitate a smooth market transition for a wide range of companies, from start-ups to large and established international organizations, who often struggle to find their first demonstration partner in a new market or jurisdiction.
High-priority clean technology sub-sectors have been identified as key to unlocking growth for Summerside. These sub-sectors include renewable energy, ag-tech, net-zero built environment, green hydrogen production and use, grid modernization, energy storage, and digitalization.
Over the next 5 – 10 years, Summerside plans to significantly grow its cleantech sector, with a particular focus on renewable energy development, green hydrogen production, and other smart and digital initiatives, aiming to reach a total renewable target of 100%.
2. Embracing Innovation and Nurturing Growth – Over recent years, Summerside has cultivated an ecosystem that celebrates entrepreneurial thinking. Fusing the city’s historic charm with a forward-thinking economic development strategy offers a conducive environment for clean businesses to thrive. The Summerside Business Commons is a testament to this commitment, positioning the city as a nexus where creativity meets sustainability. Situated in the heart of Summerside, this 14-acre Eco-Park boasts seven construction-ready lots equipped with essential infrastructures such as shared parking, phase 3 electrical, and green energy supply. It fosters innovation and success in an environment optimized for productivity and resource conservation.
3. A Hub for Diverse Sectors with a Future-forward Vision – Summerside is pushing to be Canada’s first Net Zero City and has taken an all-hands-on-deck approach, with cleantech solutions being core to the city’s economic development strategy. Summerside is on a trajectory of significant growth, with several key clean development projects underway, including satisfying the city’s energy needs with 100% renewable energy and developing the backbone infrastructure for green hydrogen production generation and fuelling stations.
Summerside has strategically decided to use the transition towards a low-carbon economy as an opportunity to develop and invest in its clean technology sector. The city is in alignment with the provincial 2040 Net Zero Framework, which further positions the city as a reliable partner and location for cleantech development and deployment. For international companies aspiring to enter the Canadian or North American market, Summerside can serve as an attractive option, offering a high-quality, supportive ecosystem and a supportive first buyer/customer opportunity. This can facilitate a smooth market transition for a wide range of companies, from start-ups to large and established international organizations, who often struggle to find their first demonstration partner in a new market or jurisdiction.
High-priority clean technology sub-sectors have been identified as key to unlocking growth for Summerside. These sub-sectors include renewable energy, ag-tech, net-zero built environment, green hydrogen production and use, grid modernization, energy storage, and digitalization.
Over the next 5 – 10 years, Summerside plans to significantly grow its cleantech sector, with a particular focus on renewable energy development, green hydrogen production, and other smart and digital initiatives, aiming to reach a total renewable target of 100%.
Looking for a Few Great Collaborators —
Key Strategic Focuses Include:
Key Strategic Focuses Include:
- Decarbonization of the Built Environment and Technologies to address existing and new developments on commercial and residential subdivision scales. Geothermal exchange for passive heating/cooling. Green building materials (e.g., low-carbon cement), district energy for hospitals, smart electric heating for municipal buildings, microgrids, smart devices and Positive Energy Districts Development.
- Renewable Energy in-city wind turbine manufacturing and deployment, building integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) cells (e.g., solar windows, sidings), small-scale geothermal energy, wastewater-derived biogas.
- Green Hydrogen HUB – Development of the full value chain, production and use of green hydrogen, Hydrogen light-duty vehicles – municipal utility fleet/public transit, refuelling infrastructure for light duty vehicles, production by freshwater/seawater electrolysis.
- Energy Storage – Community level and at-premise storage opportunities, including those in the heat pump space Mechanical, Flow, Chemical/electrochemical, Utility and Residential systems, and Battery component (hardware or software) production.
- Summerside Xchange, the city’s main accelerator and incubator program, will expand its challenge scope to include targeting advancements in both ag-tech and the built environment, areas of strategic interest for the city.
- Grid Modernization and Digitization – Software solutions to manage grid and distributed energy assets. Grid systems with two-way communication, expansion of net metering, EV to building (V2B) smart grid integration, smart street lighting, IoT for water treatment, AI-based energy management for municipal buildings, and “digital twin” of city energy and water systems.

Clean Growth Hub
The Federal Government now has a Clean Growth Hub that helps companies through the various Federal programs available to cleantech companies. The Hub is a federal focal point for clean technology, with a mandate to support companies and projects, coordinate federal programs, and improve the tracking of clean tech outcomes.
Clean technologies are defined by Statistics Canada as any goods or services designed with the primary purpose of contributing to remediating or preventing any type of environmental damage. Any goods or services that are less polluting or more resource efficient than equivalent products that provide a similar utility.
Cleantech innovators, entrepreneurs, and adopters with a project that is ready for funding can contact the Hub by submitting an online service request to obtain information about federal cleantech programs and services appropriate for their needs. If not yet ready for funding, please visit our website, which has a variety of tools and resources available.
The Hub directs clients to relevant programs but does not disperse funding, as you must apply directly to programs. We also connect clients to federal experts on questions related to regulations, standards, government procurement, skills and training, as well as programs and services related to domestic and international markets.
Organizations that will benefit from the Hub's advisory services are those that are program-ready. Program-ready means that organizations:
• have a cleantech project where the technology is past the idea stage (TRL3+);
• have a project with a defined timeline that will result in the creation of a unique product or service;
• own the Intellectual property (patent, trademark, trade secret, etc.) or have an IP strategy (when developing tech);
• have a business plan; and
• need help in identifying federal programs and services to help fill funding gaps to advance their cleantech project.
Program-ready organizations can fill out the Hub’s online service request. Organizations will follow our regular intake processes. If not yet ready for funding, please visit our website, which has a variety of tools and resources available. For questions on our service, contact our general email box, and a service officer will be in touch within 5 business days.
Summerside Quick Facts

If you are interested in learning more about investment opportunities, economic development support or opportunities for growth, please call our Economic Development Professionals.
We would love to chat.
We would love to chat.
Alternatively, you can email us at mike@summerside.ca.
It could be the most profitable email you have ever sent.
Michael Thususka
Director of Economic Development City of Summerside
275 Fitzroy Street, Summerside PE C1N 1H9
M: 902.432.0103, E: mike@summerside.ca
LET’S BUILD THE FUTURE TOGETHER!
It could be the most profitable email you have ever sent.
Michael Thususka
Director of Economic Development City of Summerside
275 Fitzroy Street, Summerside PE C1N 1H9
M: 902.432.0103, E: mike@summerside.ca
LET’S BUILD THE FUTURE TOGETHER!
